
A global team of technologists, strategists, and creatives dedicated to delivering the forefront of innovation. Stay informed with our latest updates and trends in advanced technology, healthcare, fintech, and beyond. Discover insightful perspectives that shape the future of industries worldwide.
Software Development Architecture Design:
Key Principles
This blog will explore the foundational principles of creating effective, scalable, and maintainable software systems. It will discuss common software development architecture design patterns and highlight the best use cases for each. It will also consider factors such as developer experience, scalability, and data requirements to help you choose the best approach for your software development project.
5 common software development architecture design patterns
| Architectures | Pros & cons | Use cases |
| Layered | Easy to develop and maintain, but is less scalable | Good for basic projects and smaller teams |
| Microkernel |
Flexible, secure, and adaptable, but has lower performance |
Used for embedded or automotive systems where stability is critica |
| Microservices |
Resilient, flexible, and scalable, but have increased complexity and data management challenges |
Good when fault isolation is essential and quick deployment is important |
| Event-driven |
Greater agility due to decoupled services and superior fault tolerance, but added complexity |
Useful for user interfaces such as inventory systems where real-time data distribution is critical |
| Space-based |
High-performance data access, scalable, and redundancy, but lower data consistency and increased cost |
Good for data-intensive systems including real-time analytics, financial trading, and social media |
Common software development architecture design patterns
Software architecture is the highest-level framework, or skeleton, of a software system. The software’s purpose will determine which architecture design pattern is most appropriate for its development.
Even though no two software projects are alike, certain software engineering problems recur often enough that common architecture design patterns have emerged to help solve them. Five of the most common include:
Layered architecture
A layered architecture, also known as a monolithic architecture, is the most widely used pattern because it results in code that is easy to develop and maintain. It organizes code into layers so that programs can be broken down into subtasks for each. The four most used layers are:
| Layer | Description |
| Presentation layer | The front-end user interface (UI) that handles user interactions with the application |
| Application layer | The main programs of the architecture where software developers spend most of their time |
| Business layer | The business logic that tells a system how to run the application |
| Persistence layer | The data access layer that allows manipulation of various aspects of the database |
| Database layer | Where the system stores data, indexes, and tables and performs search operations |
A monolithic architecture is a single unified codebase where all the layers are tightly integrated. It’s the standard approach that even inexperienced developers know how to work with, making it a good fit for basic software projects and smaller teams. However, this option is much less scalable and flexible than the other architectures listed below.
Microkernel architecture
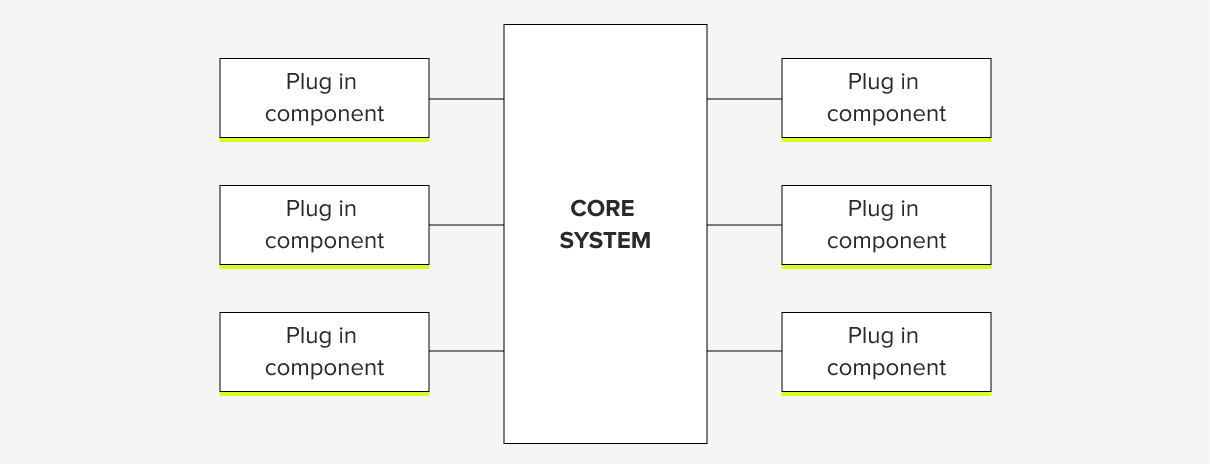
A microkernel architecture is highly flexible and adaptable. It separates applications into a minimal functional core and plug-ins with extended functionality. The core consists of standard business logic without any custom code, serving as a socket for an array of plug-ins containing specialized processing and custom features. Microkernel architectures work well for task scheduling and workflow apps, as well as software that is used for ingesting and transforming data.
Microservices architecture
A microservices architecture breaks software down into all the individual services (or microservices) that are required for functionality. Each microservice works independently of the others and can be shut down at will without affecting the rest of the application. Microservices applications are extremely flexible, resilient, and scalable, so this architecture choice is popular for cloud-native development. This architecture design provides fault tolerance because a failure in one service doesn’t crash the entire application, improving system reliability. It results in faster development and deployment, because teams can develop, test, and deploy services separately and simultaneously. Smaller, modular services are easier and more efficient to debug, update, and extend.
Event-driven architecture
An event-driven architecture is popular for applications with asynchronous data flow. It uses data-defined events to asynchronously trigger actions across distributed systems. Single-purpose event processing elements build a central unit, which accepts data and assigns it to modules that handle each specific type. Event-driven architectures are commonly used for user interfaces.
Serverless architecture
A serverless architecture involves decoupling the application layer from the underlying cloud infrastructure, so developers can build software while leaving the provisioning and maintenance of computing resources to the cloud service provider. Serverless architectures automatically scale up and down in response to demand and provide a great deal of flexibility.
10Pearls has the expertise to help you choose the best software development architecture design for your project
The software architecture is the foundation of your application, so it’s important to choose the right one for your individual needs. For example, a microservices architecture is very popular right now because of its flexibility, resilience, and scalability. However, it may not be suitable for small, inexperienced development teams that are used to more traditional architectures.
The best way to ensure you start with the best software development architecture design is to consult with expert engineers. For example, 10Pearls is a technology consulting firm with a large, global staff of software engineers who have experience with all the latest and most popular architecture patterns. Whether you just need a little help to get started or a partner to handle every stage of design and development, we’re ready to hit the ground running and deliver exceptional results.
Get in touch today to learn more about our software architecture design expertise.



